Dangerous Trojanized Tor Browser Targets E-Wallet Transactions
- Trojanized Tor swaps bitcoin wallet ID at the payment step, stealing money from its victims.
- The special version is promoted to Russian-speaking users, and it is a broken down iteration of 7.5.
- So far, the actors have made at least $40k, and their custom Tor browser is used by thousands.
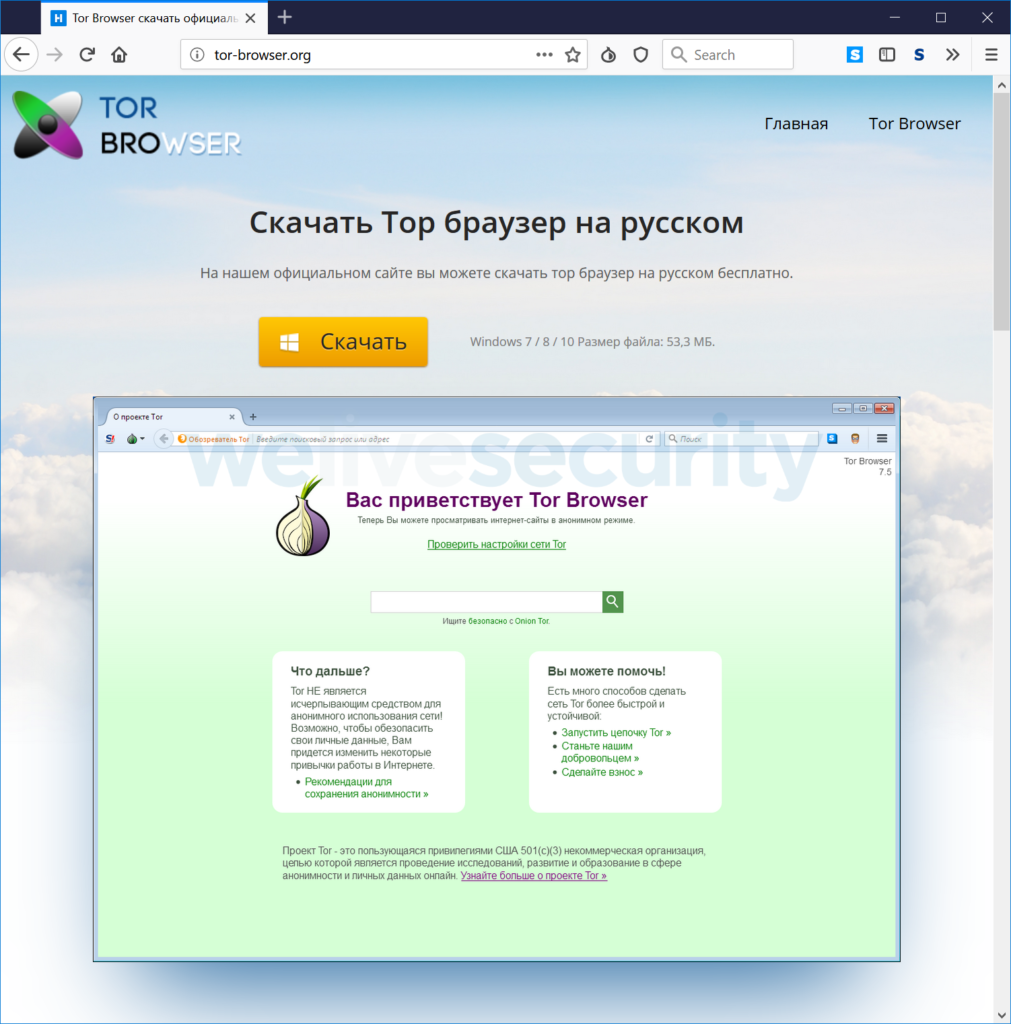
ESET researchers have discovered a Russian-language trojanized version of the Tor, which is promoted by two websites that claim to distribute the official Russian spin of the popular private browser. The websites are displaying a message which claims that the visitor has an outdated version of the Tor Browser, no matter what the actual version is. The message urges the visitor to click on the “update” button and download the supposed latest version, which is nothing other than a trojanized version of the browser. The malicious websites are “torproect[.]org” and “tor-browser[.]org”, both created back in 2014.
Source: WeLiveSecurity
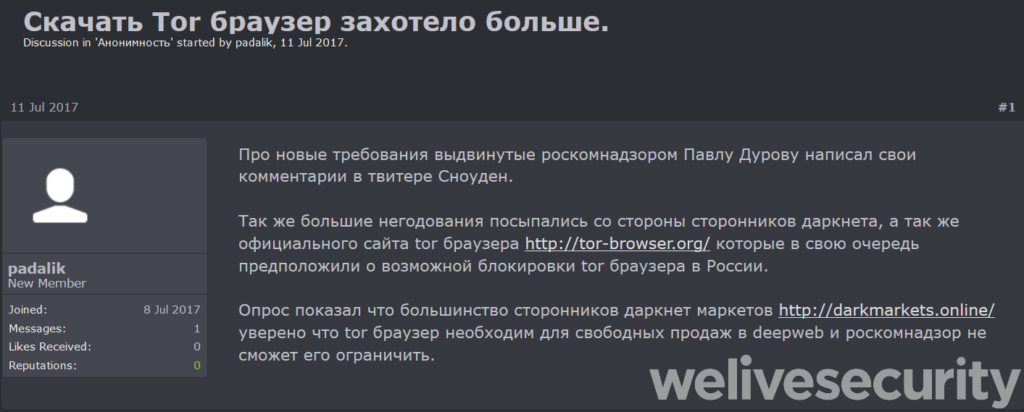
The two websites are aggressively promoted on Russian forums where the actors spam the darknet market message boards, cryptocurrency discussions, internet privacy, censorship bypassing boards, etc. The actors even tried to put their websites on search results, by publishing Pastebin documents that contained the URLs and quite a lot of keywords. The crooks are even making false promises such as an anti-captcha capability. The truth is that the trojanized Tor browser that the actors are trying to distribute is based on version 7.5, which was released back in January 2018. Besides the default settings and some of the extensions that have been changed, all else remains stock.
Source: WeLiveSecurity
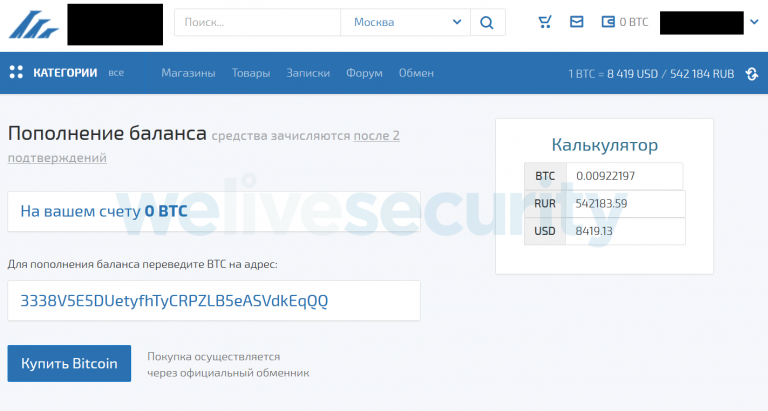
The changes include the disabling of auto-updates, as that would damage the trojanized browser immediately. Another change concerns the digital signature check, and how to render it inactive so that the door to installing whatever add-on they want opens widely. One of the key add-ons that they use is a modified version of the “HTTPS Everywhere”, which injects a monitoring script in every webpage the victim visits. This information is sent to the C2 server, so as the actors can decide on what to do next. What they’re doing is to use a JavaScript payload that can exfiltrate form filling information, scrape data, display fake messages, etc. The goal of all the above is to steal crypto from the victims, hijack e-wallets, swap bitcoin payment account address with theirs, and more. According to ESET’s investigation, the actors have made at least $40k so far, but the actual amount could be a lot bigger.
Source: WeLiveSecurity
If you want to use the Tor browser, you should download it from the official website, and trust nothing else. Whatever languages and localization are supported officially will be available there, so there’s no reason to use “special” versions from shady sources. Almost always, these tools will get you into trouble, no matter how legitimate they may look at first sight.
Do you have anything similar to report to us? Feel free to share your information with us in the comments down below, or on our socials, on Facebook and Twitter.