Security Researchers Discover Malware Targeting Samsung Service Centers
- Two security research companies have released reports that detail a malware campaign and exploit chain meant for Samsung service centers.
- Both Russian and Italian service centers have also been attacked in a similar fashion, and it is likely that the same culprits are behind both incidents.
- The research companies have yet to conclude their investigations, and there are no signs of any data theft as per the preliminary reports.
Hackers are attempting to inject malicious code into computers of Samsung service centers in Italy and Russia. The purpose behind the attacks is unknown, and investigations are ongoing to find the culprits. Two security research teams revealed the details of the attacks in recently in separate reports. The malware seeks to take advantage of the CVE-2017-11882 Office Equation Editor vulnerability.
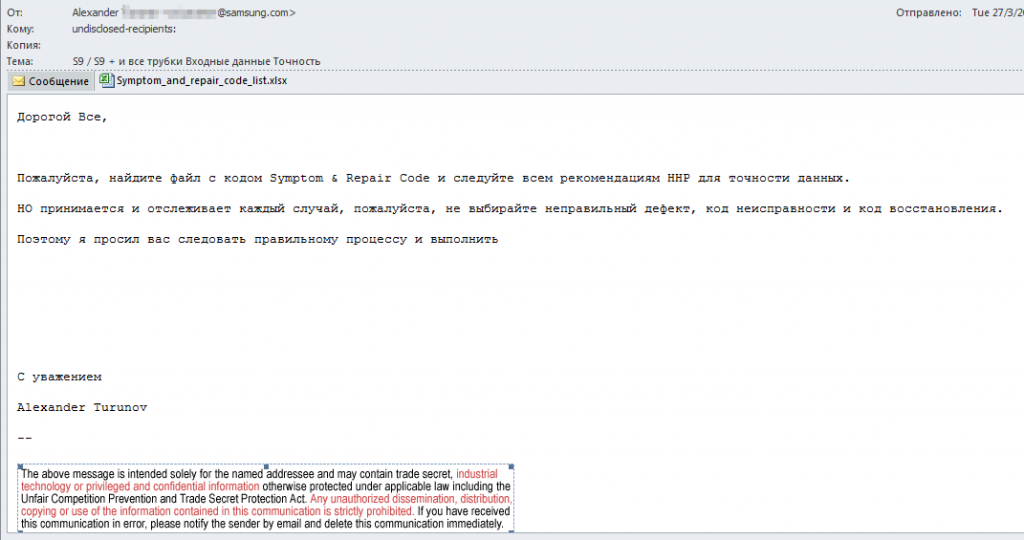
Hackers initiate the malware attack by sending phishing emails to service centers with infected Microsoft Excel files. The attacks were first initiated in March 2018 in Russia and Italy using RAT malware. Russian service centers were attacked by Imminent Monitor RAT malware while Italian service centers were targeted by nJRAT and Netwire. The malware code was discovered to be written in native Russian and Italian instead of English.
Image Courtesy of Fortinet
According to American research company Fortinet “A distinctive feature of these attacks is their multi-staging. These attacks use forged emails, malicious Office documents with exploits for a vulnerability that is 17 years old, and a commercial version of a RAT that is tucked into five different layers of protective packers.”
The security research teams who discovered the malware have been investigating the attacks, but neither TG Soft or Fortinet have been able to identify what the hackers are after. Both countries hold very little customer information in the service centers which hackers may benefit from. One of the possible motives might be to infect Samsung mobile devices with malware to steal personal information. However, there has been no proof of any such activities by the hackers.
Why do you think the hackers are trying to inject malware at Samsung service centers? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below. To get the latest updates on tech, follow TechNadu’s Facebook page, and Twitter handle.