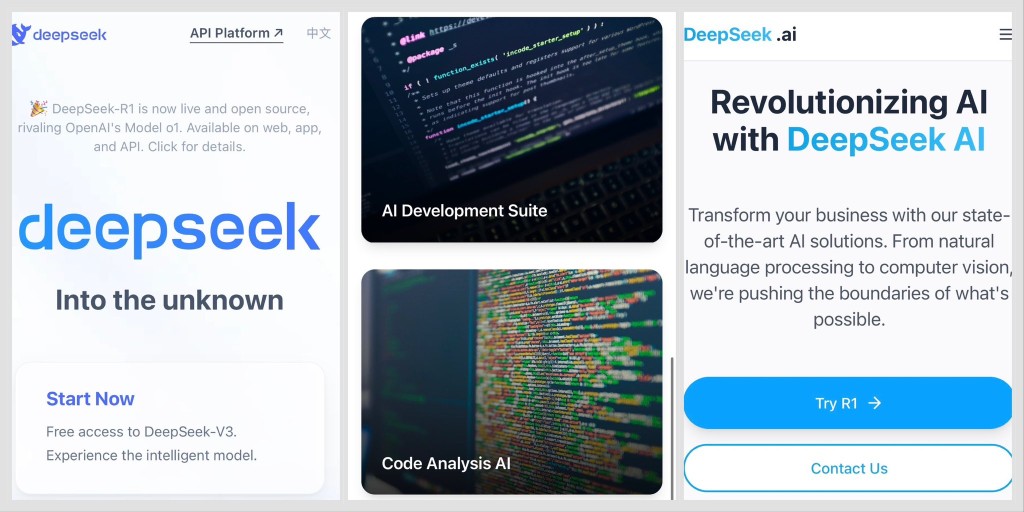
Phishing Alert: Beware of Cloned Websites of DeepSeek R1 AI Model
- China-made AI model DeepSeek R1 has been targeted by cybercriminals with cloned websites.
- A cybersecurity analyst found several phishing websites that could be used to scam users.
- One of the websites ends with an .org extension – /deepseek[.]org.
The latest AI model made in China, DeepSeek R1 has been cloned by threat actors. Cybersecurity researcher Dominic Alvieri listed names of the cloned copies.
These are the duplicated versions of the DeepSeek R1, the famed AI model offered as open-source:
- /deepseek[.]ai
- /deepseek[.]org
- /deepseek[.]app
- /deepseek[.]top
- /deepseek[.]cyou
- /deepseek.website
- /deepseekai[.]com
- /deepseekagent[.]com
The presently unknown threat actors targeted the latest version DeepSeek R1 to which Alvieri exclaimed, “Companies spend tens of millions of dollars developing ideas but can’t spend @ $100 to secure their digital domain and help prevent employees and customers from getting phished.”
Deep Seek R1 has become a global phenomenon for its performance and giving a tough competition to ChatGPT. Among the first versions of DeepSeek was DeepSeek Coder, launched in 2023 and used for coding projects.
Newer versions – including DeepSeek LLM and DeepSeek-V2, which were launched last year – took the large language model market to another level for its low cost.
Cloning a website can lead to data exposure and financial loss if unsuspecting users input their details on them.
Such phishing websites appear similar to a legitimate website and are often sent to targets as links in malicious emails, SMSes, and pop-ups.
In a recent incident, MasterCard took a step in time to prevent abuse of its platform after a security consultancy found a typo in its domain name and notified the payment card company.
If threat actors had understood about the domain name typo, they would have used the correctly spelled domain name and created fake websites to cheat users.