North Korean Lazarus Group Targets Developers with New Wave of Malicious ‘npm’ Packages
- North Korea's Lazarus Group has launched a new wave of malicious cyberattacks targeting Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- These focus on devs through npm packages in a continuing effort to compromise development ecosystems.
- The packages included BeaverTail malware and deployed the InvisibleFerret backdoor.
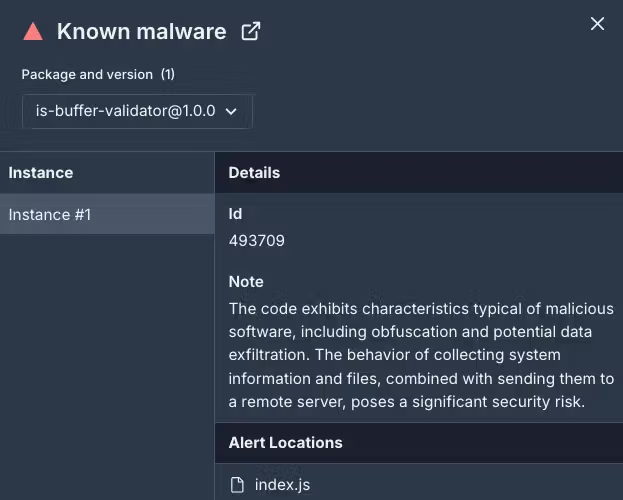
Six additional malicious npm packages were attributed to Lazarus Group in a wave of recent cyberattacks–is-buffer-validator, yoojae-validator, event-handle-package, array-empty-validator, react-event-dependency, and auth-validator.
They were designed to infiltrate development environments, steal credentials, and deploy malware. Together, they were downloaded over 330 times before being reported by The Socket Research Team.
The packages mimic trusted libraries, such as the is-buffer-validator filter for empty buffers resembling the popular is-buffer library. This deliberate similarity aims to trick developers into unknowingly downloading the malicious software.
The packages included BeaverTail malware with a secondary deployment of the InvisibleFerret backdoor, enabling long-term access to compromised systems–similar to the ‘DeceptiveDevelopment’ campaign that targeted freelance developers.
These packages targeted Windows, macOS, and Linux environments, increasing the scope of potential victims.
GitHub repositories linked to the packages further added to their veneer of legitimacy. Five of the malicious packages had associated repositories, and all were hosted under accounts resembling credible development profiles.
The malicious GitHub repositories are:
- github.com/edan0831/is-buffer-validator
- github.com/alximmykola379/yoojae-validator
- github.com/alextucker0519/array-empty-validator
- github.com/elondavid888/react-event-dependency
- github.com/kevin-tra/auth-validator (defunct)
The tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) observed in this campaign align with Lazarus Group’s previous operations. Key indicators include advanced obfuscation, multi-stage payload delivery, and persistent data theft mechanisms.
The malware specifically targets browser login data, cryptocurrency wallets, and sensitive system information, transmitting the data to command-and-control (C2) servers.
Examples of Lazarus's familiar methods in this campaign include the deployment of identical obfuscation and code-hiding techniques used in previous attacks, malicious script behavior resembling prior campaigns targeting supply chain vulnerabilities, and organized typosquatting strategies aimed at open-source ecosystems.