Google Spoofed Via DKIM Replay Attack and OAuth Infrastructure Flaw Exploit
- A sophisticated attack was recently seen impersonating Google in phishing emails.
- Attackers use Google’s OAuth to generate signed and seemingly legitimate emails from Google.
- To build credibility, these lead recipients to a Google Sites link via a legal court case lure.
Cybercriminals have leveraged vulnerabilities in Google’s infrastructure to execute a highly sophisticated phishing attack, leaving users exposed to credential theft. Initially, Google declined to address these vulnerabilities, but later agreed to fix the OAuth bug.
This phishing campaign exploits two main weaknesses in Google’s ecosystem, using them to masquerade as legitimate communications via valid, signed emails and malicious use of Google Sites.
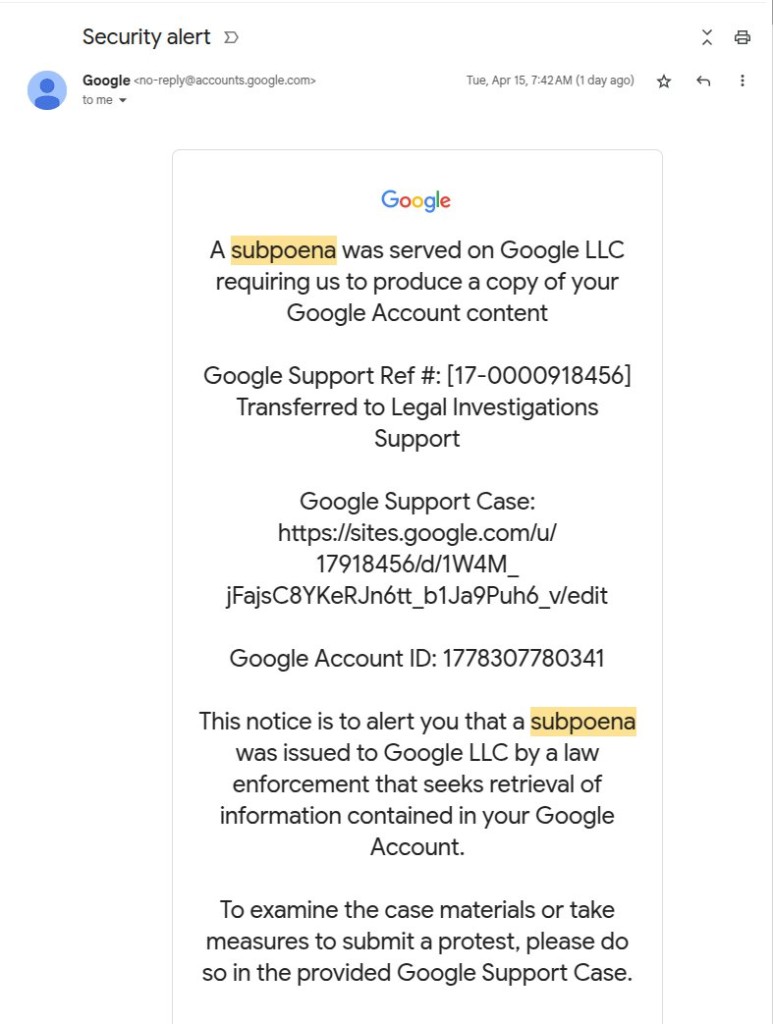
Attackers use Google’s OAuth mechanisms to generate legitimate-looking emails from [email protected], with valid DKIM signatures. Gmail's security checks pass these emails as authentic, displaying no red flags to users.
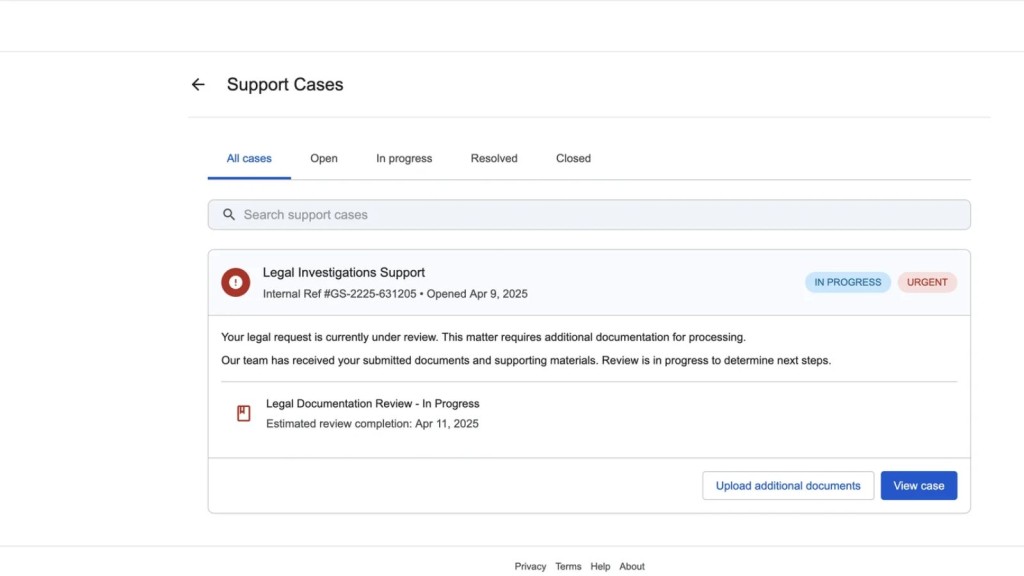
Hackers host counterfeit "support portal" pages on Google’s Sites platform. These pages mimic legitimate Google interfaces, leveraging the trusted “google.com” subdomain to deceive users.
Attackers register a Google OAuth app with the entire phishing message embedded in the application name.
They grant this app permission to their Google account, triggering a genuine “Security Alert” email from Google sent to their account. This signed email is forwarded to victims, who see it as legitimate due to its valid signatures.
Links in the email direct users to a fake support portal hosted on sites.google.com. Here, users encounter cloned Google login pages that harvest their credentials upon entry.
Google’s infrastructure design permits abuse of its systems in a manner that deceives even savvy users. It combines the credibility of Google’s domains with cleverly engineered steps to obscure malicious intent. Users trust the “google.com” domain implicitly, yet this trust is being weaponized.