GitHub Phishing Campaign Employs Security Alert Lure to Install Malicious OAuth Application
- Hackers are actively targeting developers on GitHub through a phishing campaign.
- The threat actors use a security alert lure as a persuasion method, asking for a password change and enabling 2FA.
- The goal is to make targets install a malicious OAuth app that requires granting dangerous permissions.
A sophisticated phishing campaign has targeted nearly 12,000 GitHub repositories, leveraging fake "Security Alert" issues to trick developers into authorizing a malicious OAuth application, granting attackers full control over accounts and source code.
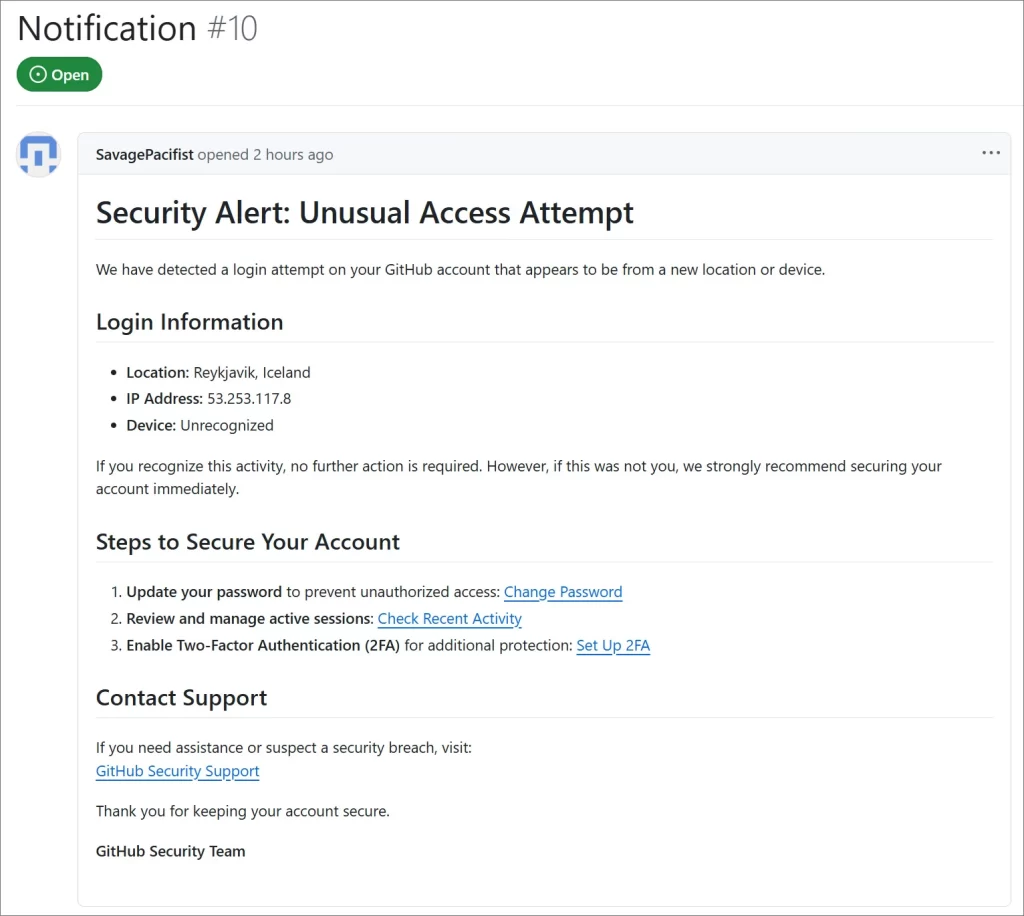
This scam exploits developers’ trust by issuing warnings of “unusual account activity” from Reykjavik, Iceland, accompanied by an IP address (53.253.117.8).
The alerts claim the affected users’ accounts have been breached, urging them to update credentials, review active sessions, and enable two-factor authentication.
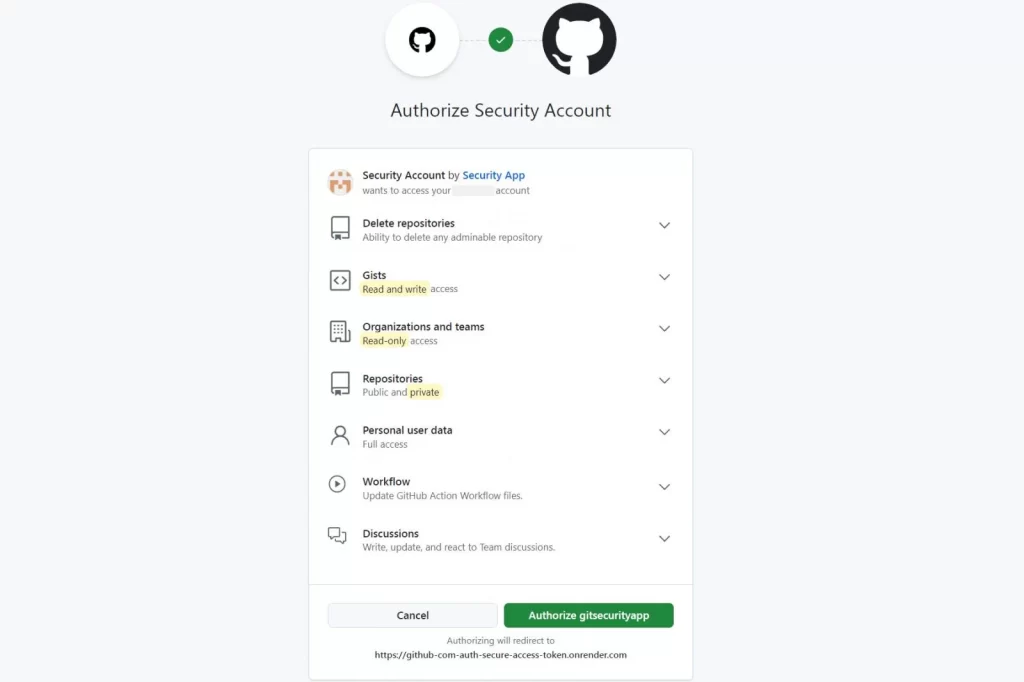
Clicking the provided links directs users not to GitHub-secured settings but to an authorization page for a deceptive OAuth app dubbed "gitsecurityapp."
Upon authorization, the attackers gain access to an alarming range of privileges, including:
- Full control of repositories (public and private)
- Read/write access to user profiles and discussions
- Deletion of repositories
- Access to GitHub gists
- Control over GitHub Actions workflows
The campaign was first identified by cybersecurity researcher Luc4m and began at approximately 6:52 AM ET on March 16, 2025.
GitHub appears to be responding to the situation, as reports indicate fluctuations in targeted repositories. However, the phishing operation remains active and ongoing.
Individuals who accidentally authorized the malicious application are advised to take immediate action and revoke its access via GitHub Settings → Applications (remove unfamiliar or suspicious OAuth apps, particularly those resembling “gitsecurityapp”).
Victims of this attack can also check their GitHub Actions workflows for unexpected or malicious modifications and look for any newly created private gists that could harbor malicious intent.
Of course, refreshing all compromised tokens and credentials to secure account access is also essential moving forward.
GitHub was exploited by threat actors throughout the last months for malicious ad campaigns or distributing malware such as Lumma Stealer, Vidar Stealer, SectopRAT, and Cobeacon.