Fake Hiring Challenge for Polish Developers Steals Sensitive Data via FogDoor Backdoor
- Hackers leverage a fake coding test called "FizzBuzz" to lure victims into downloading a malicious ISO file.
- The campaign deploys the persistent FogDoor backdoor used for data theft and remote command execution.
- While the dissemination method is unknown, it is believed the threat actor uses professional platforms and forums.
Cybercriminals use fake hiring challenges to infiltrate target systems and extract sensitive information, likely via job platforms like LinkedIn or regional developer forums. A GitHub repository masquerades as a legitimate coding test, specifically targeting Polish-speaking developers.
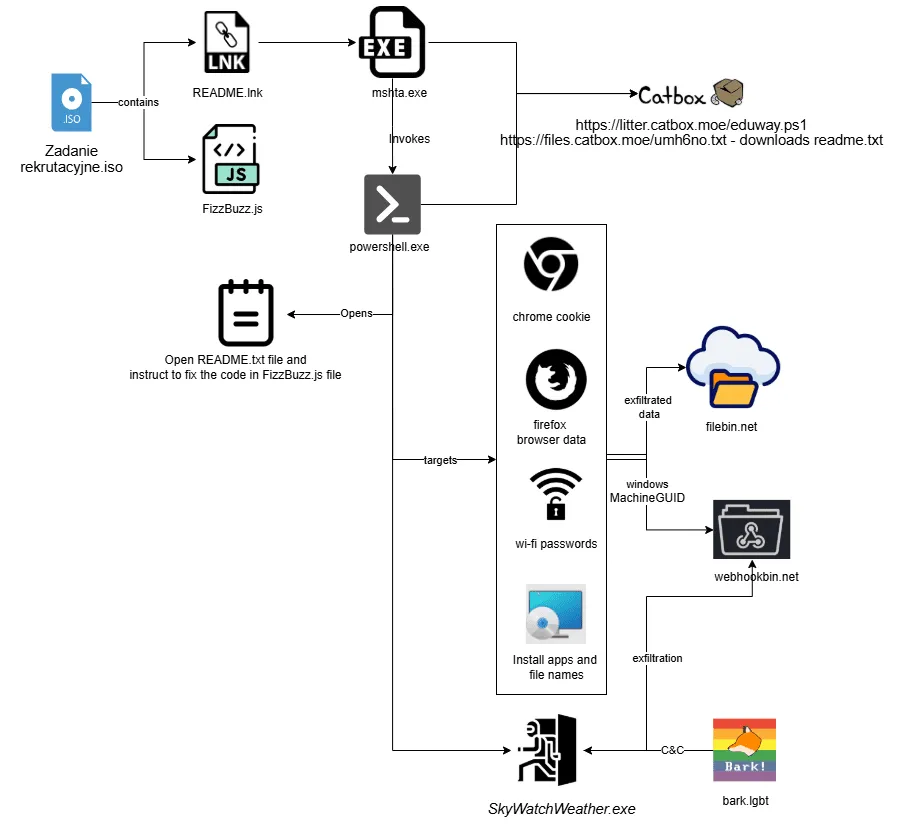
Cyble's Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) identified this alarming campaign that employs a fake coding test called "FizzBuzz" to lure victims. Once developers download the provided ISO file, it contains a JavaScript exercise and a malicious shortcut file labeled “README.lnk.”
Executing the shortcut triggers a PowerShell script that downloads and installs "FogDoor," a stealthy backdoor designed for persistence, data theft, and remote command execution.
Unlike traditional malware operations that depend on command-and-control (C2) servers, FogDoor uniquely uses a Dead Drop Resolver (DDR) technique, utilizing social media profiles as its C2 infrastructure. This approach makes detection and takedown efforts more challenging to execute.
The malware also employs geofencing technology to restrict execution to specific regions, currently targeting victims in Poland. Once active, FogDoor systematically retrieves and exfiltrates browser cookies, Wi-Fi credentials, and system data from infected machines.
Upon execution, the PowerShell script opens a decoy "README.txt" file designed to appear harmless while the backdoor is installed.
Then, it downloads an executable file saved as “SkyWatchWeather.exe” in the victim’s public downloads folder and sets up a scheduled task named “Weather Widget,” configured to execute the backdoor every two minutes indefinitely.
FogDoor communicates with a temporary webhook service and monitors a social media platform for commands, reinforcing its evasion techniques by leveraging unconventional C2 channels.