When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
Encryption Basics and You: Everything You Need to Know
Encryption, encryption, encryption. Everyone seems to be going on about this important security technology these days. However, I’m sure not every person on the planet who should know about digital encryption has the time to delve deeply into the subject, so we’ve put together the most important things you need to know about encryption right here. This isn’t everything there is to know about encryption, buy it is everything you need to know about encryption.
The Cliff Notes on What Encryption Is
You can get a more complete explanation of encryption in our encryption explanation article. Here, however, I’ll just go over the basic details.
Encryption is a concept about as old as written history. It’s the art of using some method of systematic scrambling to prevent other people from reading information. If one person wanted to let someone far away know secret information, they would encrypt the message. The person at the other end knows how to unscramble your message so that they can get the original information back.
The simplest form of encryption is probably the substitution cipher. This is where you take every letter in your message and substitute it for something else. If you don’t know which letters are swapped with which then it can take a long time to figure out how to unscramble the text.
Modern encryption is much more sophisticated and comes in two major types if we’re talking about digital encryption on computers.
The Subtypes of Encryption
Modern encryption solutions center around encryption keys. This is a string of letters, numbers and symbols that can be used to unscramble the encrypted information. In general, there are two main approaches to using encryption keys: symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric encryption solutions have only one key. That same key both encrypts and decrypts the information. Your WiFi password is an example of such a key. Symmetric encryption is fast and efficient, but if you can’t keep the key secret it falls apart. So if you want someone far away, who you can’t secretly pass the key, to use encryption you need a different solution.
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of mathematically-linked keys. You encrypt with one key and decrypt with the other. So if you only have one key, all you can do with it is to encrypt information. In practice, one key is made public, so that you can send secure information. You then use your private, secret key to unlock the information again. This is how we can do secure encryption across the web.
Where Does Encryption Come From?
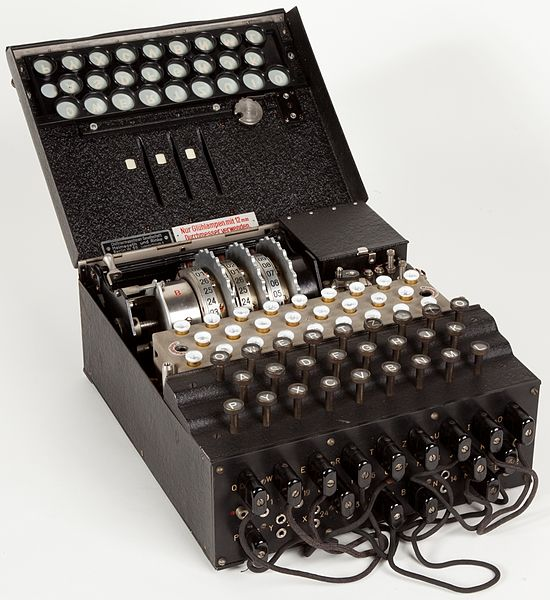
Enigma Machine Image By Alessandro Nassiri [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
The peak if pre-computer encryption has to the German Enigma machine. This mechanical device constantly changes the cipher and could quickly process relatively complex encryption. Near the end of the war, an Allied scientist named Alan Turing finally figured out how to crack the code, laying the Axis communications bare. Turing is also, not by accident, considered one of the fathers of modern computing. While true digital computers never got a chance to help with the WWII war effort, the work done during that period moved their advent forward.
Once we started connecting computers together, it became ever more clear that digital encryption would become a crucial feature. In 1978 the DES algorithm was created, Although flawed and weak by modern standard, this was the foundation of modern strong encryption.
Why Not Everyone Loves Encryption
Source: Pixabay
For many players on the global stage, encryption is a double-edged sword. Yes, it’s a powerful way to keep your enemies out of your secrets, but it also means you can’t spy properly on them.
It’s not just enemy players either. Governments are very motivated to keep an eye on the people within their borders. There are many excuses for this, such as preventing major terror attacks or otherwise protecting everyone else.
Since even the richest governments don’t have the technology to crack the sort of encryption normal people have access to, they try to keep their options open through legal means. For example, in some countries, it is a crime if you refuse to decrypt a hard drive or phone if the court orders you to. Governments may also force providers who use encryption to protect their customers to include so-called “back doors” in their software so that they can spy on citizens, criminal or otherwise.
Encryption Protects Your Internet Connection
The widest application of encryption is without a doubt internet communication. When you visit your bank’s website, for example, the address will start with “https”. This is an encryption standard that makes all of the data between you and that site secure. Not all sites are secured like this, but it is quickly becoming the norm.
VPN or virtual private networks offer a way to also hide all of your internet traffic from both your service provider and the government who might compel them to release records about what you’ve been doing, As an added bonus, the VPN provider will also help you stay anonymous from the point of view of the site you are visiting. If you're looking for a good VPN, we recommend ExpressVPN.
Can Encryption Be Broken?
In principle, the encryption standards we use today can be broken. In practice, they are so complex that no computer system in the world has enough power to put a dent in it. So if you are using industry-standard encryption to protect your data, there is no real practical way for it to be broken into.
That does not mean that there are no ways to get around encryption. The theft of keys is one of the main weaknesses in encryption. The back doors I mentioned before are another way your encryption can be bypassed. If you use biometrics like fingerprint readers to unlock your encrypted, then, of course, you can be forced to provide your finger or eye for scanning. Weak passwords are another major cause of encryption defeat, which can be prevented by using a strong password.
One day radical machines such as quantum computers could also provide a way to break current encryption technology. For now, however, it’s good enough for government spy agencies.
Encryption Can Be Used To Attack
While we generally think of encryption as something to protect us, some cybercriminals have found a way to weaponize encryption in quite a devastating way. It’s called ransomware. This cyber attack method is estimated to hit a cost of $11.5B by 2019. So it is a really big deal.
How does it work? The attacker uses malware to quietly encrypt the victim’s files. When it finished that job, you’re presented with a message to either a cough up an amount of money or lose all your data forever. It’s one of the nastiest cyber attacks possible and the fight to keep it at bay is still ongoing. The best personal defense is to keep your most valuable data backed up on a cloud storage solution. However, even the likes of DropBox and Google can be problematic!
Encryption Providers Can Read your Stuff
Services like DropBox and VPN providers are two examples of companies that use encryption to provide you with a service. So no one can access your files from outside without your credentials. That is, no one but you and the company providing the service.
You see, as long as you are not the sole holder of your encryption keys, you have to trust that the company itself is not using your information to exploit you. Even if your files are only indexed and processed as part of big data analysis, there may still be a fundamental privacy principle violated here.
The answer is to use end-to-end encryption services which don’t have the keys but leave them in your care.
What Sorts of things need Encryption?
What sorts of things should you encrypt? In general, anything that contains information you would not want people to see without your permission should be encrypted. These include:
- USB flash drives
- USB hard drives
- Cloud storage accounts
- Your internet connection
- Phones and tablets
- Computer hard drives
These are all common items and services we use every day. Without encryption, they are all an opportunity to steal your information. Which means encryption is absolutely essential.
Now You Know
There you have it! You should now know the most essential facts about encryption and how it impacts your daily life. If you feel like you want to go deeper, we have plenty of articles here on TechNadu that delve much deeper into the aspects of encryption I’ve listed above. If not, you’re set!