Cybercriminals Impersonate Google Ads in Promoted Results to Exploit Advertiser Accounts
- Security researchers have identified three malicious campaigns leveraging hijacked Google advertiser accounts.
- The threat actors impersonate Google Ads via Sponsored results as a lure.
- Their objectives revolve around phishing and/or malware distribution.
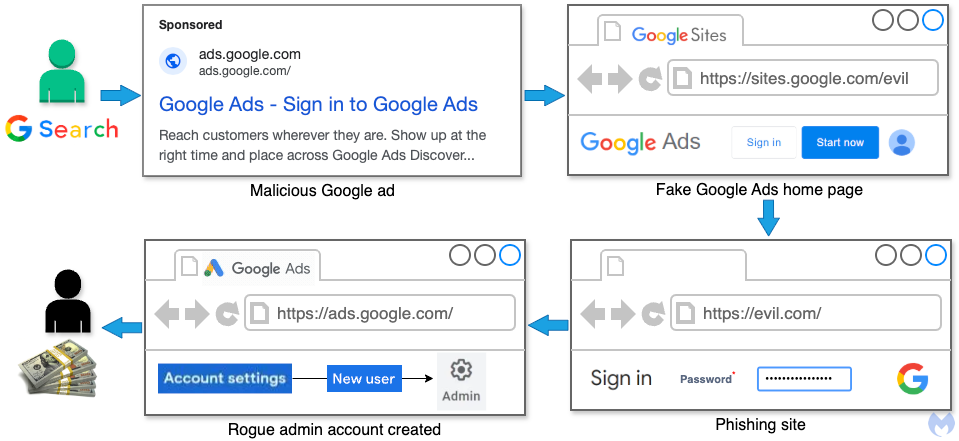
Fake ads impersonating Google Ads redirect victims to counterfeit login pages to steal advertiser account credentials. Once compromised, these accounts are either resold on blackhat forums or kept by attackers to sustain and expand their fraudulent activities.
Experts tracking this scheme have identified it as one of the most egregious malvertising campaigns to date, impacting thousands of advertisers worldwide.
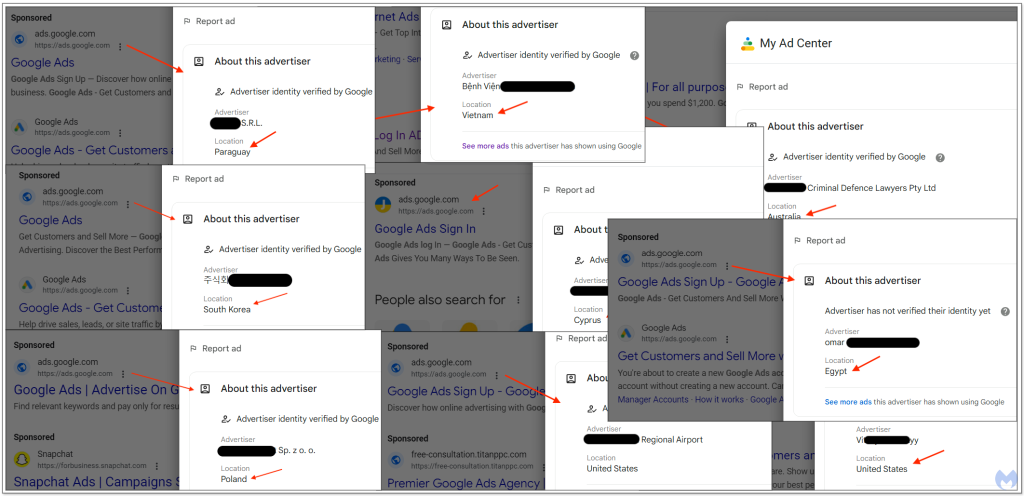
The phishing operation first raised suspicion when malicious ads claiming to be for Google Ads itself appeared in search results. Extensive investigation revealed a widespread campaign leveraging fraudulent "Sponsored" results that convincingly impersonate Google.
These fake ads target both new and existing Google Ads users, offering sign-up or login options that appear legitimate. Clicking on these ads redirects users to a counterfeit Google Ads homepage hosted on Google Sites, a free platform that attackers exploit to bypass domain authentication rules.
This loophole enables the fraudulent ads to appear indistinguishable from legitimate ones. On the fake page, users are invited to "Start now," after which they are redirected to a phishing site designed to steal login credentials.
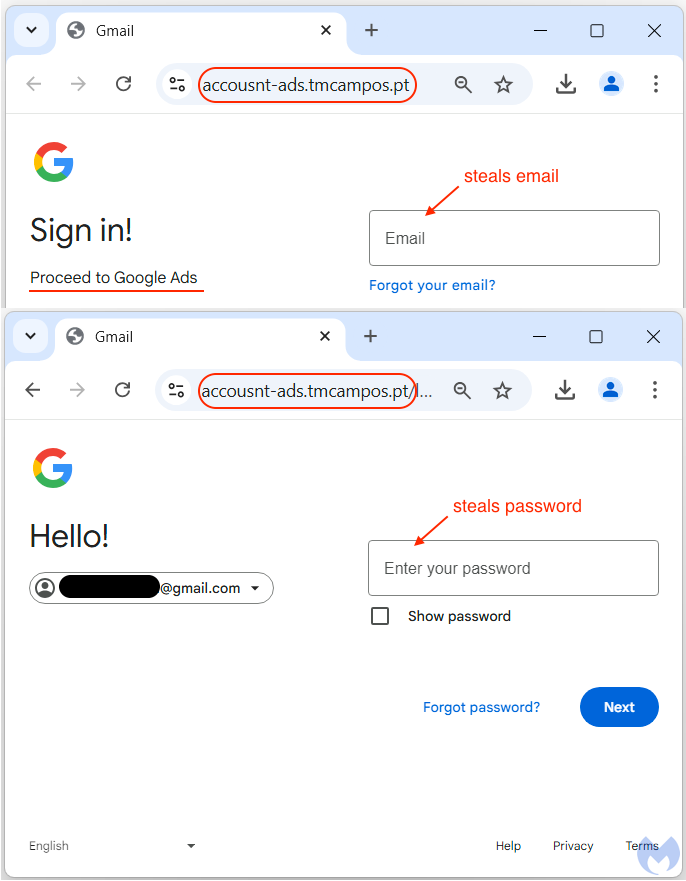
Using a phishing kit embedded with JavaScript, attackers collect users' credentials, cookies, geolocation, and other identifying data. The stolen information is then transmitted to a remote server.
Victims of this scam experience the following sequence of events:
- The user inputs account credentials into the phishing page.
- The phishing kit extracts unique identifiers, cookies, and account details.
- An email alerts the victim of a suspicious login attempt, often from a Brazilian IP address.
- If the victim does not act quickly, attackers add a new administrator to the Google Ads account using a different Gmail address.
- Attackers proceed to exploit the account, locking out the victim and potentially running up substantial ad charges.
Analysis indicates two major groups orchestrating this operation, with the most prolific likely operating out of Brazil. The second group appears to be Asia-based, using advertiser accounts from Hong Kong.
A third variation of this campaign involves distributing malware instead of hijacking accounts, suggesting that some threat actors may be employing this method in a temporary capacity.
Despite ongoing efforts to report and mitigate these incidents, malicious ads continue to surface relentlessly, including for Slack, Google Safety Center, and Google Authenticator.