Critical NVIDIA Container Toolkit Vulnerability Allows Full Access to Host System
- A newly discovered exploit can bypass a fixed NVIDIA Container Toolkit flaw - CVE-2025-23359.
- The flaw’s risks include potential code execution, privilege escalation, DoS, and data tampering.
- Researchers say hackers could break out of a container's isolation protections and gain full system access.
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a bypass for a previously patched security vulnerability in the NVIDIA Container Toolkit. The flaw tracked as CVE-2025-23359 could allow threat actors to break out of a container's isolation protections and gain full access to the host system.
This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 8.3 and poses significant risks, including potential code execution, escalation of privileges, denial of service, information disclosure, and data tampering.
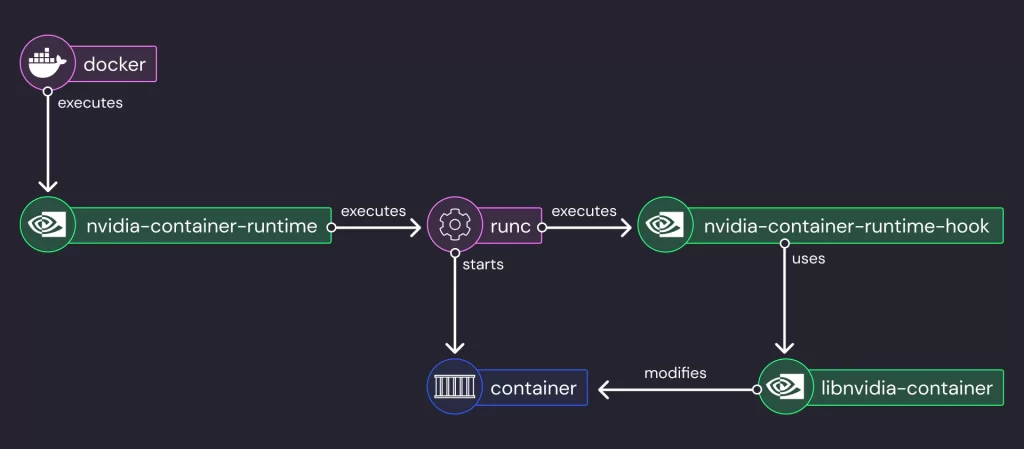
NVIDIA’s advisory on Tuesday explained, "NVIDIA Container Toolkit for Linux contains a Time-of-Check Time-of-Use (TOCTOU) vulnerability when used with default configuration, where a crafted container image could gain access to the host file system."
The newly discovered flaw constitutes a bypass for an earlier vulnerability (CVE-2024-0132, CVSS score 9.0), which NVIDIA addressed in September 2024. Cybersecurity firm Wiz, whose researchers uncovered the issue, elaborated on the threat's mechanism and potential exploits.
The vulnerability enables attackers to mount the host's root file system into a container, granting full read-only access to all files. The researchers—Shir Tamari, Ronen Shustin, and Andres Riancho—found that this access can be escalated for full host compromise by interacting with runtime Unix sockets.
The researchers explained, "Our source code analysis revealed that the file paths used during mount operations can be manipulated with symbolic links, making it possible to mount directories outside the container, such as the host's root directory, into a container path like '/usr/lib64'."
While the default behavior restricts access to read-only, attackers can leverage Unix sockets to spawn privileged containers, bypassing this limitation entirely. Through this elevated access, they could perform critical operations such as monitoring network traffic, debugging processes, and executing host-level commands.
The vulnerability impacts:
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit: Versions up to and including 1.17.3 (fixed in version 1.17.4)
- NVIDIA GPU Operator: Versions up to and including 24.9.1 (fixed in version 24.9.2)