Critical Kubernetes Vulnerability in Ingress NGINX Controller Exposes Thousands of Clusters to Attack
- Critical unauthenticated RCE flaws were discovered in the Kubernetes Ingress NGINX Controller.
- The vulnerabilities stem from flaws in the admission controller component of the tool.
- A new cybersecurity report says vulnerable cloud environments utilizing Kubernetes are exposing over 6,500 clusters.
A set of severe vulnerabilities, collectively dubbed IngressNightmare, in the widely used Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes. These unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) flaws, tracked as CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-1098, CVE-2025-24514, and CVE-2025-1974, have been assigned a CVSS score of 9.8.
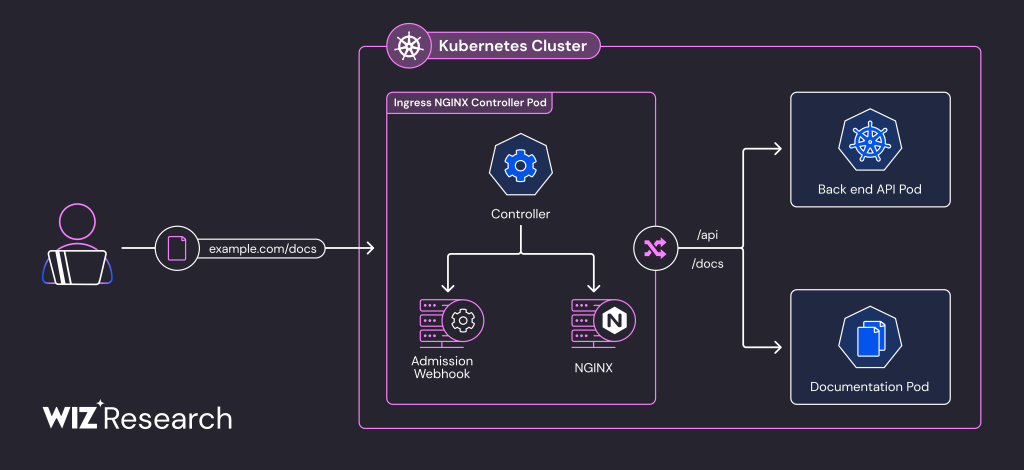
Ingress NGINX Controller is a core Kubernetes project responsible for routing external traffic to services within Kubernetes clusters. With its prominence highlighted in Kubernetes documentation and over 18,000 stars on GitHub, the tool is a popular choice for managing ingress configurations.
However, researchers at WIZ Research estimate that 43% of cloud environments utilizing Kubernetes are vulnerable, exposing over 6,500 clusters, including those of Fortune 500 companies, to potential compromise.
The vulnerabilities stem from flaws in the admission controller component of the tool. This component, designed to validate ingress objects before deployment, is accessible by default over the network without authentication.
Exploitation allows attackers to inject malicious NGINX configurations via crafted ingress objects, executing arbitrary code on the cluster's pod and gaining unauthorized access to sensitive secrets across all namespaces. This provides a direct path to complete cluster takeover.
The vulnerabilities, which allow the injection of malicious NGINX directives into configuration files validated by nginx -t, demonstrate how attackers could exploit these flaws to upload and execute malicious libraries with elevated privileges.
Wiz disclosed the issues to Kubernetes beginning December 31, 2024, working collaboratively to resolve them. Updated internal patches and versions were released in early 2025.
The public disclosure was finalized on March 24, 2025, ensuring adequate mitigation steps were in place before making the vulnerabilities known.