Critical 7-Zip Vulnerability May Circumvent Windows MotW Security Measures
- A severe 7-Zip flaw permits the bypass of the Mark-of-the-Web security feature in Windows.
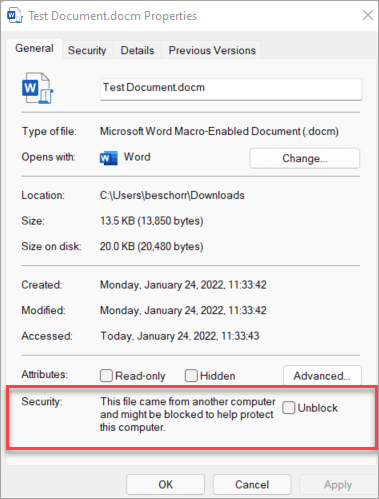
- Archives downloaded from untrusted sources may carry a flagged Alternate Data Stream, but nested archives go around the security measures.
- Users are urged to patch this critical vulnerability manually, as 7-Zip does not include an auto-update feature.
A critical vulnerability in the widely-used file archiver 7-Zip enabled attackers to bypass the Mark-of-the-Web (MotW) security feature in Windows. Exploiting this now-patched flaw leaves users' systems exposed to potential malware threats.
The MotW is a security mechanism implemented by Windows to protect users from files originating from untrusted locations, such as those downloaded from the internet or sourced from restricted zones, according to the latest Malwarebytes security report.
Files flagged with the MotW prompt security warnings to alert users of potential risks, such as running unverified executable files or opening malicious documents.
When applied to Microsoft Office documents, the MotW activates Protected View, which automatically enables read-only mode and disables macros. Macros, when enabled, can be exploited by attackers to execute malicious code on an unsuspecting victim's system.
The flaw in 7-Zip also revolves around the handling of the MotW attribute. Archives downloaded from untrusted sources may carry the ADS (Alternate Data Stream) containing the MotW flag. However, attackers have historically exploited vulnerabilities in file archivers to strip the ADS during decompression, bypassing the MotW protections.
This specific vulnerability required attackers to use specially crafted nested archives. A nested archive contains another archive that needs to be opened within it. By decompressing such nested files, the ADS containing the MotW flag would fail to propagate, negating the security warnings or protections typically triggered by the MotW.
The exploitation of this vulnerability further demanded user interaction, such as visiting a malicious webpage or opening a malicious file, putting users at risk if they unknowingly interacted with attacker-supplied content.
To mitigate the risk, 7-Zip users should confirm they are running version 7-Zip 24.09 or later, where the bug has been patched. Unfortunately, 7-Zip does not include an auto-update feature, which means users must download and install the latest version manually from the 7-Zip downloads page.
Recently, a Proof-of-Concept was leaked online for a zero-day exploit that targets the LZMA decoder within 7-Zip and allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on a victim’s machine when malicious 7Z archive files are opened or extracted.