Booking.com Customers Targeted by Phishing via Compromised Partners’ Accounts
- Booking.com customers can be targeted by phishing and scamming campaigns to steal sensitive details.
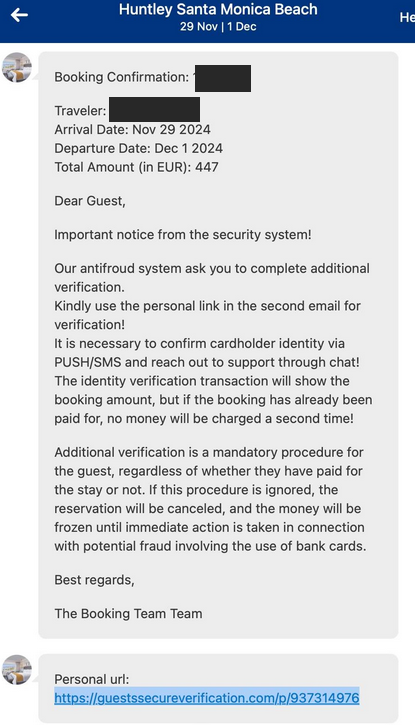
- Recently, a partner’s account with the service was compromised, and hackers impersonating the hotel sent customers to a fake website.
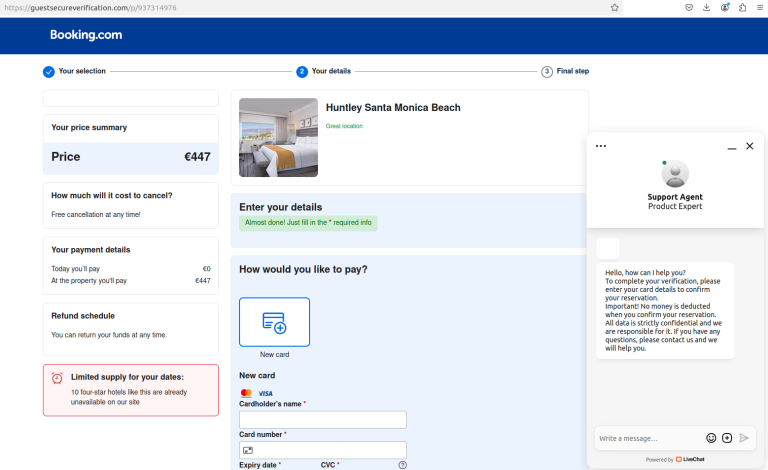
- There, they tried to collect payment information under the guise of additional checks.
Phishing attacks targeting the hospitality sector have taken a sophisticated turn, with cybercriminals leveraging stolen credentials from Booking.com partners to deceive and defraud customers. In a recent spear-phishing campaign, cybercriminals exploited stolen credentials from a California hotel partnered with Booking.com.
They tricked unsuspecting customers into providing sensitive information by posing as legitimate booking confirmations that required fake additional verification, according to a report from Krebs on Security.
The malicious message contained a URL that led to a phishing website impersonating the Booking.com reservation page of the compromised vendor.
Booking.com acknowledged the breach and emphasized that its internal systems remained uncompromised.
According to SecureWorks, phishing attacks on Booking.com partners have surged since March 2023, often driven by data-stealing malware. These attacks align with a broader trend identified by Booking.com, which reported a 900% increase in phishing attempts targeting travelers.
In response, Booking.com has enforced two-factor authentication (2FA) for partners, aiming to secure access to sensitive data. However, questions remain about the consistency of its implementation across all partners. The lack of mandatory 2FA has been a critical factor in allowing unauthorized access to partner accounts, leading to fraudulent transactions and data breaches.
The growing sophistication of these attacks highlights the urgent need for businesses in the hospitality sector to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. Implementing comprehensive security protocols, educating employees about phishing threats, and enforcing stricter access controls are vital to mitigating these risks.
Cybercriminals, armed with new AI tools, are refining their tactics to outsmart traditional security measures. Scammers also recently targeted the booking service, sending malware-ridden messages to hosts and even creating fake properties to collect sensitive user data leveraging generative AI tools.