AI-Powered Rhadamanthys Stealer Adds Optical Character Recognition, Targets Crypto Wallets
- The Rhadamanthys infostealer upgraded to optical character recognition technology.
- The malware uses AI capabilities to get multiple crypto wallet seed phrases via images.
- Marketed as a malware-as-a-service tool, Rhadamanthys now integrated 30 wallet-cracking algorithms.
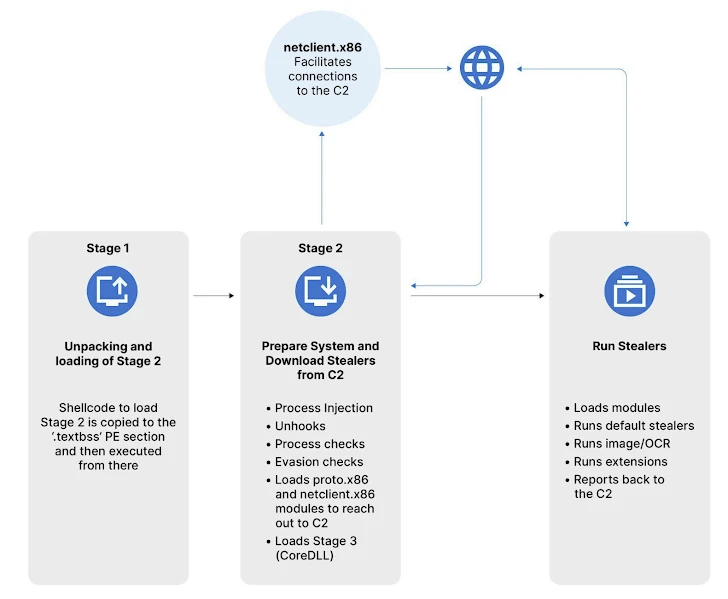
The Rhadamanthys information stealer has integrated advanced AI capabilities, now employing optical character recognition (OCR) technology that allows extracting wallet seed phrases from images—a process dubbed "Seed Phrase Image Recognition," according to an analysis by Recorded Future's Insikt Group.
The malware's version 0.7.0, released in June 2024, utilizes AI-driven text extraction to identify multiple saved phrases, expanding its potential victim pool. This latest version represents a complete overhaul of both client-side and server-side frameworks, enhancing execution stability and integrating 30 wallet-cracking algorithms.
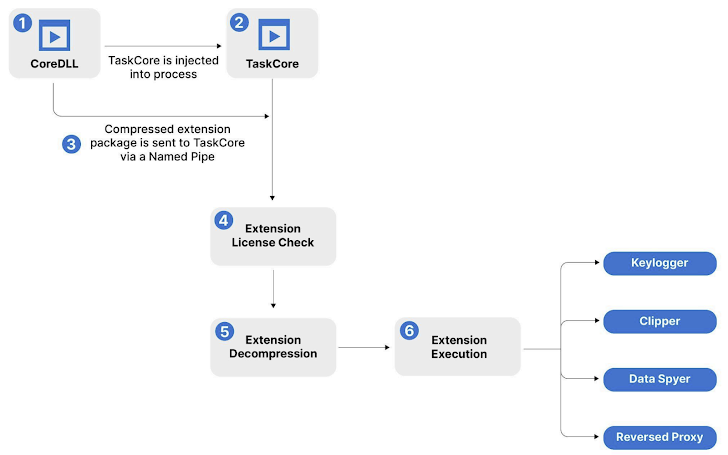
Rhadamanthys is further equipped with a dynamic plugin system that adds capabilities such as keylogging, cryptocurrency clipping, and reverse proxy functionality, making it a preferred tool for cybercriminals.
The addition of AI-powered graphics and PDF recognition, coupled with the ability to execute Microsoft Software Installer (MSI) files, underscores the malware's sophisticated evasion techniques. These updates complicate analysis in sandboxed environments, posing challenges for traditional security solutions.
The malware's developers have also shown agility in adopting novel attack vectors, such as drive-by download campaigns that deceive users into executing PowerShell commands via misleading CAPTCHA pages. The criminal group Marko Polo has exploited these developments, orchestrating over 30 scam campaigns targeting cryptocurrency sectors.
Rhadamanthys remains widely used and is marketed under a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model despite being banned from underground forums like Exploit and XSS due to targeting Russian entities.
Subscriptions for this powerful tool, developed by "kingcrete," are priced at $250 per month or $550 for 90 days. It continues to harvest a wide array of sensitive data, including system information, credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, browser passwords, and cookies.
Concurrently, the cybersecurity landscape sees other threats evolving. Google-owned Mandiant highlights Lumma Stealer's use of customized control flow indirection to thwart analysis tools. Meanwhile, information stealers like Meduza, StealC, Vidar, and WhiteSnake have been updated to bypass security mechanisms in Chrome.