Hackers Use Telegram as Malicious C2 Centers to Distribute ‘Nova’ Malware
- Threat actors increasingly move to trusted platforms for Command-and-Control communications.
- A security researcher infiltrated a threat actor's Telegram-based C2 channel, which they used to exfiltrate infostealer and keylogger data.
- Security researcher Ben Folland managed to access screenshots and key logs from the threat actor’s desktop.
Hackers increasingly adopt trusted platforms such as Telegram, Slack, and Discord to route communications from their malware and execute Command and Control (C2) functions. Their association with well-known, trusted services enables attackers to bypass standard network defenses.
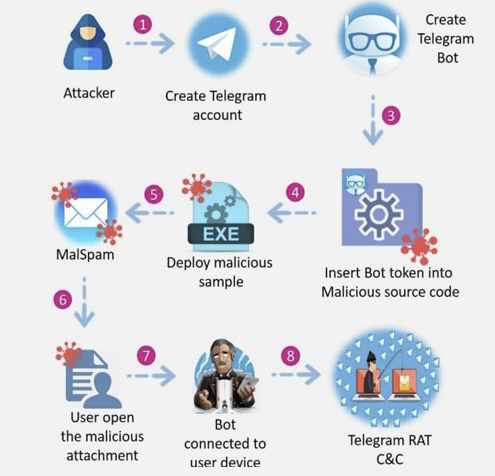
Platforms like Telegram allow malware to camouflage its activity, hiding in plain sight. Telegram-based C2 malware typically operates through these phases:
- Bot Setup: Attackers create a bot through Telegram’s BotFather service, obtaining a unique bot token.
- Malware Deployment: The bot token is embedded into the malware, which is then distributed to victims.
- Command Polling: The infected device queries Telegram servers for new commands.
- Data Exfiltration: Stolen data or results are sent via Telegram, completing the feedback loop for the attacker.
These techniques are actively exploited in real-world scenarios. Low-tier attackers (known as "script kiddies") aggressively employ this tactic to distribute info stealers and keyloggers and gather sensitive credentials or credit card data.
High-profile groups, such as the Lazarus Group, have even leveraged Telegram for remote access trojans (RATs), cementing its relevance as a primary C2 mechanism.
By analyzing malware samples embedded with Telegram bot tokens sourced via platforms like VirusTotal, Ben Folland was able to infiltrate the attackers' communications channels. One operator even tested malware on their own machine, inadvertently leaking critical screenshots and log data.
This lapse provided direct insight into the attacker's infrastructure, including associated phishing campaigns and malicious domains, and methods used for credential harvesting, such as phishing schemes that utilized malicious Telegram-integrated bots.
It also showed operational mistakes that showcased how the malware interacted with production systems, revealing specific tactics and procedures. Analysis revealed backend infrastructure that was used to disseminate mass phishing emails.
The analysis presented a study case where a phishing email impersonating DHL contained the Nova malware–a recently discovered derivative of the infamous Snake Keylogger–within a .7z attachment.
The Nova malware has demonstrated elevated levels of sophistication and capabilities to exfiltrate data over FTP or Telegram. This tool relies heavily on process injection, payload decryption with TripleDES, and credential theft from browsers like Chrome.