Notorious Lumma Stealer Spreading Rapidly Through Telegram Channels
- Hackers can very easily disseminate a notorious infostealer via a simple vector such as Telegram channels.
- One channel pretends to offer cracked software that hides the Lumma Stealer malware instead.
- The malware bypasses basic detection mechanisms by connecting to an obfuscated Steam account for its C2 communication.
A powerful information-stealing malware is proliferating via Telegram channels. Hackers can easily distribute Lumma Stealer via the popular messaging and sharing app, reaching a broad audience while bypassing traditional detection mechanisms, with India being most affected by this threat, followed by the U.S. and Europe.
The latest security report from McAfee underlines how Lumma Stealer’s spread through Telegram channels demonstrates abusing prominent services to distribute malicious code to a broad audience is extremely easy.
McAfee detects these fake crack software as [Trojan:Win/Lummastealer.SD].
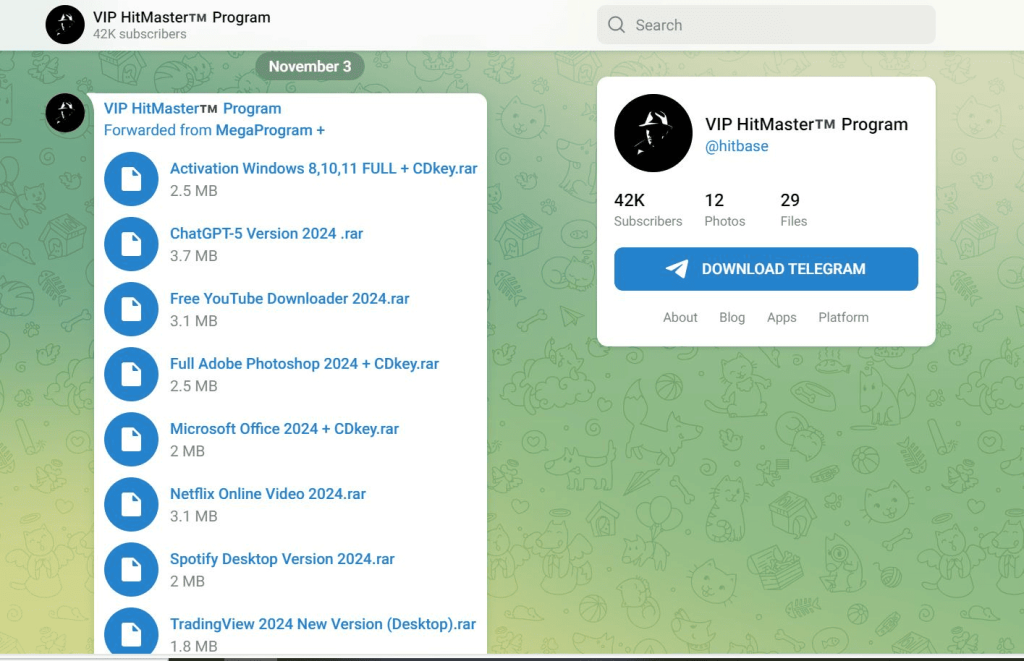
One Telegram channel that offers malware disguised as crack software (https[:]//t[.]me/hitbase), with 42,000 subscribers, is related to another one that distributes malware to benign users (https[:]//t[.]me/sharmamod) with 8,660 subscribers. These two channels are forwarding messages from each other.
Since the others are similar in nature except for the theme, the report tackles a specific file, CCleaner 2024.rar, which contains a Readme.txt with the link to the telegram channel and an exacutable -- CCleaner 2024.exe is a .NET application.
The two-stage malware writes two .NET file payloads: “XTb9DOBjB3.exe” (Lumma_stealer) and “bTkEBBlC4H.exe” (clipper), which employ the same decryption logic as the main file (ccleaner).
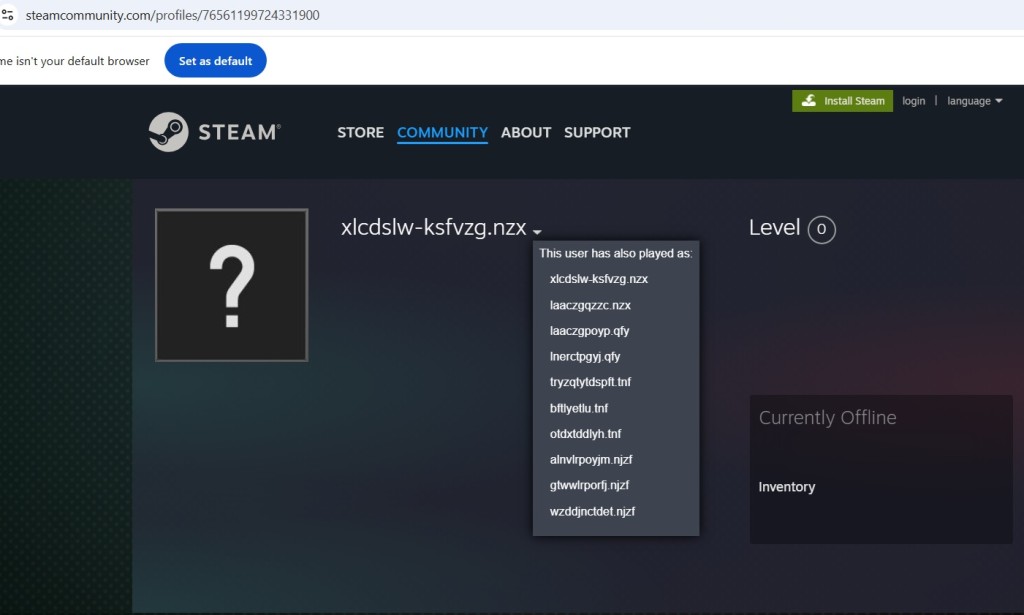
One of the domains it connects to is a Steam community page whose user name was obfuscated and had many aliases. The malware extracted the initially obfuscated Steam account name and decoded it to reveal the C2 domain, effectively bypassing basic detection mechanisms to evade detection by traditional security solutions.
Lumma Stealer can exfiltrate sensitive information and compromise user privacy. Infostealers are one of the main malware types used by threat actors, and Lumma Stealer, StealC, and Vidar Stealer were among the most seen this year.