New HardBit Ransomware 4.0 Variant Now Comes Enhanced with Password Protection
- Security researchers observed an enhanced version 4.0 of the HardBit ransomware group.
- This version is improved with password protection and delivered via Neshta.
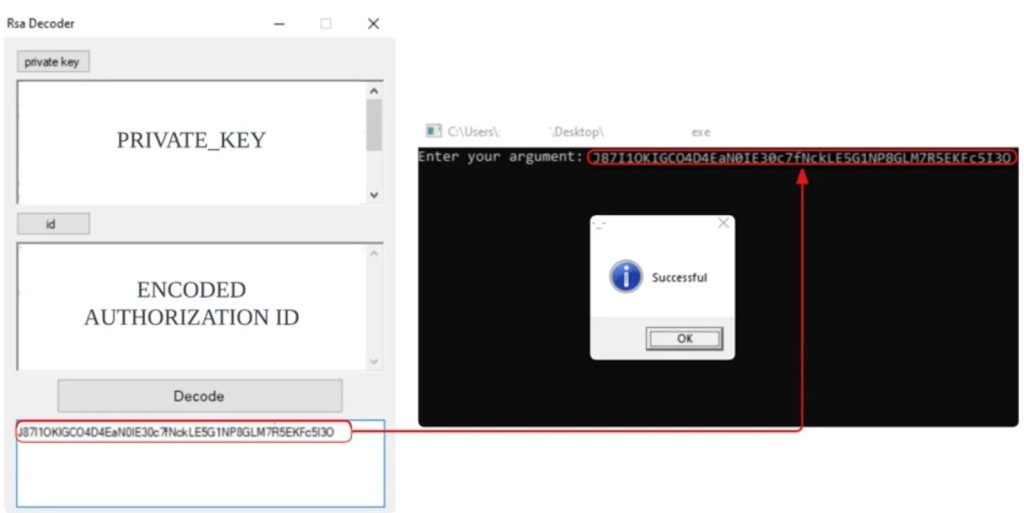
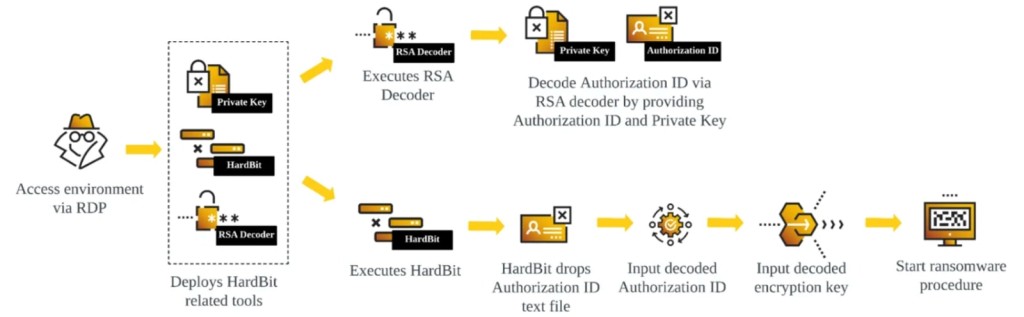
- An RSA decoder binary and a Private Key are delivered for an encoded authorization ID.
The HardBit ransomware group enhanced version 4.0 now comes with passphrase protection, which Cybereason observed in the wild, with all the binaries packed by the Neshta virus. The HardBit binary provides an encoded authorization ID and a Private Key to decode it with the help of an RSA decoder binary.
The HardBit Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) was first seen in 2022 and is used for financially motivated attacks. It usually exfiltrates and encrypts victims' data for ransom and threatens to conduct additional attacks.
There are CLI or GUI versions of the ransomware available, the latter being more intuitive for operators without strong technical skills.
HardBit’s initial infection method is not well known, but security researchers believe threat actors use the brute force of an open RDP and SMB service due to multiple login failures from known brute-forcing IP addresses observed in the compromised environment.
Then, they use the Windows credential dumping tool Mimikatz and the RDP brute-forcing tool NLBrute for lateral movement. They also deployed a malicious BAT script that has been observed in GoGoogle ransomware but did not execute NirSoft and LaZagne.
The threat actors retrieved the Advanced Port Scanner, the popular port scanning tool KPortScan 3.0, and malicious network shares scanning 5-NS new.exe network discovery tools from the Internet. The latter were previously employed by Dharma Ransomware, LockBit Ransomware, and Phobos Ransomware.
Neshta, a virus known to have been active since 2003, is responsible for delivering HardBit. HardBit is itself a .NET binary obfuscated by a popular packer used by Redline Infostealer and Cyborg ransomware. Security analysts believe it may be a custom version of the Open-Source .NET packer ConfuserEx.
The observed version of Neshta dumps the HardBit Ransomware binary into the %TEMP% directory with the same filename as the original Neshta binary. Once the dumping of HardBit Ransomware is complete, Neshta proceeds to execute HardBit Ransomware via ShellExecuteA.
HardBit contains features to disable Windows Defender’s Tampering Protection, Anti-Spyware, and Real-Time monitoring by updating registries.
This ransomware group shares similarities such as name, group image, fonts, and ransom notes with LockBit ransomware, and security experts believe the latter may have served as an inspiration for HardBit.