Set of 9 Vulnerabilities Called “Name:Wreck” Affects Over 100 Million Devices
- Researchers warn about a set of critical vulnerabilities affecting millions of IoT devices.
- The flaws can result in RCE and DoS situations, taking control of the target devices or taking them down.
- Patching everything is practically impossible, so applying mitigations is the only way to go now.
Experts from the Forescout Research Labs and the JSOF Research team have discovered a set of nine DNS-related vulnerabilities affecting four popular TCP/IP stacks (FreeBSD, Siemens Nucleus NET, IPnet, and NetX), and by extension, over 100 million IoT, OT, and IT devices that rely on them. Called “Name:Wreck”, the flaws introduce denial of service and remote code execution risks, enabling actors to take full control of the vulnerable devices or render them useless.
The set of the identified vulnerabilities are the following:
- CVE-2020-7461: FreeBSD RCE affecting message compression. CVSS v3.1 score – 7.7
- CVE-2016-20009: IPnet RCE affecting message compression. CVSS v3.1 score – 9.8
- CVE-2020-15795: Nucleus NET RCE affecting domain name label parsing. CVSS v3.1 score – 8.1
- CVE-2020-27009: Nucleus NET RCE affecting message compression. CVSS v3.1 score – 8.1
- CVE-2020-27736: Nucleus NET DoS affecting vDomain name label parsing. CVSS v3.1 score – 6.5
- CVE-2020-27737: Nucleus NET DoS affecting domain name label parsing. CVSS v3.1 score – 6.5
- CVE-2020-27738: Nucleus NET DoS affecting message compression. CVSS v3.1 score – 6.5
- CVE-2020-25677: Nucleus NET DNS cache poisoning affecting transaction ID. CVSS v3.1 score – 5.3
- No CVE ID assigned yet: NetX DoS affecting message compression. CVSS v3.1 score – 6.5
As for the vulnerable stacks, the researchers can confirm the following versions as exploitable:
- FreeBSD 12.1
- IPnet VxWorks 6.6
- NetX 6.01
- Nucleus NET 4.3
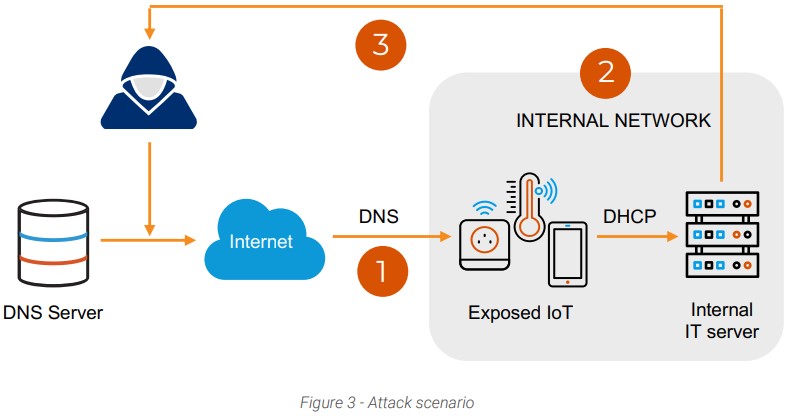
A typical attack would begin with a DNS request to a vulnerable server, resulting in the establishment of initial access to the organization’s network. From there, lateral movement in the network becomes possible via code execution and DHCP requests. And finally, the attacker could perform data exfiltration from the compromised servers.
The estimated impact on product categories covers mobile phones, various IoTs used in home or office, retail automation systems, industrial automation solutions, communication and networking, aerospace and defense, automotive and transportation, and even medical devices. The researchers clarify that the 100 million estimate is very conservative and that, in reality, the number of the affected devices could be way higher.
Patching them all is also very complicated, if not outright impossible. It would require identifying what OS is running on the IoT devices, obtain the versions of currently installed packages, and then push updates down to the consumer level. Even if the patches trickle down from the stack vendor to the device's firmware, considering those devices aren’t centrally managed, the fixing patches will need to be manually applied. For example, medical and industrial control systems that are rarely taken offline are very unlikely to ever apply such fixes.
What this leaves us with is mitigations, so here are the suggestions of the researchers:
- Identify devices running the vulnerable stacks using the open-source script from Forescout Research Labs.
- Enforce segmentation controls and proper network hygiene.
- Monitor progressive patches released by affected device vendors and devise a remediation plan for your vulnerable assets that balances business risk and continuity requirements.
- Configure devices to rely on internal DNS servers as much as possible and closely monitor external DNS traffic.
- Monitor all network traffic for malicious packets that try to exploit known vulnerabilities or possible zero-day threats affecting DNS, mDNS, and DHCP clients.