Microsoft Has Released “Patch Tuesday” for September 2020
- Microsoft has released another big patch, fixing two dozen critical flaws and a hundred essential bugs.
- There are no reports about any of these vulnerabilities having been discovered and already exploited in the wild.
- Applying the patch as soon as possible should be a priority, but not before you backup.
Microsoft has released this month’s security fixing patch for its array of products, addressing a whopping 129 vulnerabilities. About 24 of the fixed flaws are categorized as critical, so applying the updates as soon as possible should be non-negotiable, as always.
The patch covers problems in Windows, the SQL Server, Visual Studio, the JET engine, Edge, Internet Explorer, the Office suite, Azure DevOps, ASP.NET, OneDrive, MS Dynamics, and the ChakraCore. No zero-days that were actively exploited in the wild have been discovered and fixed this month.
The most notable fixes are the following:
CVE-2020-0922: A remote code execution vulnerability affecting “Microsoft COM” and based on how the component handles objects in memory. An attacker could exploit this flaw using a malicious JavaScript file and tricking the target into opening the website where it’s hosted. CVSS score – 8.8.
CVE-2020-1057 and CVE-2020-1172: Both of these are RCEs existing in the ChakraCore scripting engine, possibly leading to memory corruption due to improper object handling in memory. Can lead to privilege escalation, up to full user rights.
CVE-2020-1508 and CVE-2020-1593: Flaws in the “Media Audio Decoder,” triggered by visiting an attacker-controlled web page or by opening a specially crafted document.
CVE-2020-1193, CVE-2020-1218, CVE-2020-1332, and CVE-2020-1594: Vulnerabilities plaguing the MS Office (Excel and Word), and which can be exploited via phishing attacks. Opening malicious attachments could trigger exploits of these flaws, leading to remote code execution.
CVE-2020-1115: A privilege escalation bug that exists on the “Windows 10 Common Log File System”. An attacker would use a malformed CLFS log file to cause a pool overflow and execute code onto the victim’s machine.
CVE-2020-1152: Another privilege escalation flaw that exists in the DirectComposition subsystem of the Win32k.sys driver file. An integer overflow can lead to use-after-free memory corruption and the eventual acquisition of rights to execute commands on the target machine.
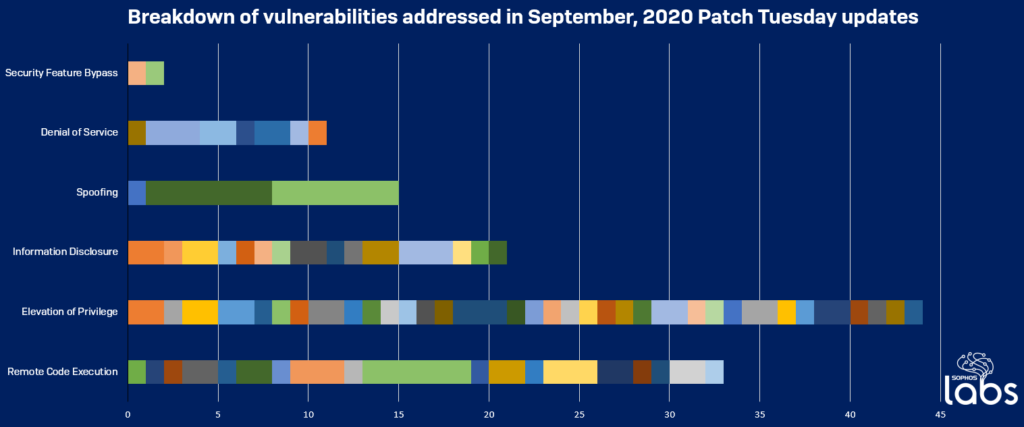
Sophos has prepared the following diagram to give users an idea of what types of flaws this month’s patch addresses.
Source: Sophos
Before you proceed with the patch’s application, remember that taking a backup right now wouldn’t be bad. Sometimes, fixing patches introduce glitches that cause serious disruption, so better be prepared than sorry.
In any case, applying this month’s patch shouldn’t be delayed, as hackers now have another 129 clues on how to target and compromise unpatched systems.
Read More:
- Microsoft Flight Simulator – A Quick Review of the Most Advanced Flight Sim Ever Released
- Microsoft Steps Into the Heated Battle Between Apple and Epic
- Microsoft May Soon Pull the Plug on the 32-bit Version of Windows 10