Microsoft Pushes Fix for Critical “Wormable” RCE in Windows DNS Server
- Microsoft has released the July 2020 patch, and it comes with over a hundred critical and important bug fixes.
- One of the nastiest is a wormable DNS server flaw that affects a wide range of Windows Server releases.
- Microsoft has provided a registry-based workaround for those who can’t apply the patch.
Microsoft has released this month’s patch for Windows, and the update brings 123 fixes. The most notable and scary of all is the CVE-2020-1350 vulnerability, which is a critical remote code execution flaw in the Windows DNS server.
Microsoft classified this flaw as “wormable,” giving it a CVSS score of 10.0. This means an exploit to a vulnerable DNS server could lead to infections and subsequent exploits to other connected systems, propagating the exploit through a “worm.”
The problem with CVE-2020-1350 lies in the way that Windows DNS servers handle requests, so all that an attacker has to do to exploit the weakness would be to send a specially crafted request to the target server, triggering an integer overflow problem. The parsing of DNS signature queries on SIG PR records fails to validate the length in the record packet, allowing a portion of it to remain in the attacker’s control.
Of course, no in-depth technical details were given on this for security reasons, but that doesn’t mean you should delay the application of the available patch. If that’s impossible for any reason, Microsoft has provided a registry-based workaround, although it isn’t perfect. Those who handle TCP-based DNS response packets that exceed a 65Kb size should opt for the patch anyway.
This flaw affects every version between Windows Server 2008 and 2019, and so it includes releases that are no longer supported by Microsoft. Due to the extreme severity and the wormable nature of the discovered flaw, though, the patches cover these products as well.
Source: Sophos
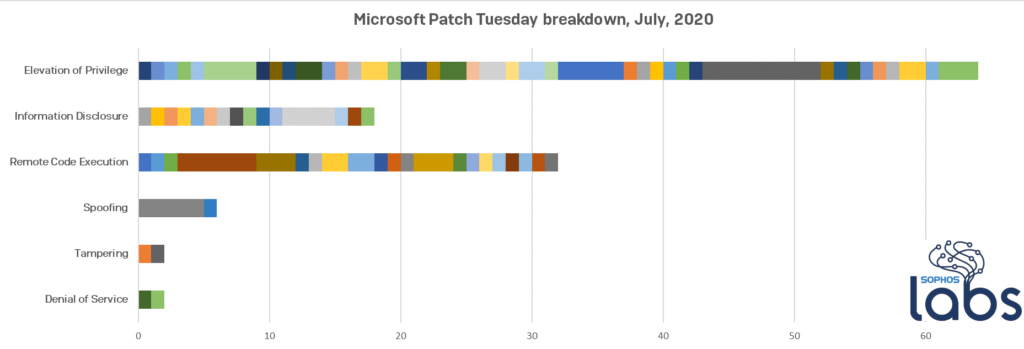
Besides that flaw, Microsoft has addressed another 19 critical bugs and a whopping list of 103 vulnerabilities that were classified as important. The fixes cover every component of Windows, from the Jet database engine and the GDI+graphics subsystem to the Internet Explorer and various kernel driver modules.
As for the type of flaws that were addressed this time, most of them are elevation of privilege issues, with remote code execution coming second, and information disclosure problems along with spoofing completing the picture.
Related: Microsoft Returns With Another Whopping Patch Tuesday for June
As Microsoft clarified, none of the flaws they fixed with this month’s patch were observed to be under active exploitation in the wild. Despite this, you are advised to apply the available patch as soon as possible, which is always the proper thing to do, no matter what other protection tools or security solutions you’re using.