Around 165 Snowflake Customers Impacted in the Data Theft Incident Attributed to UNC5537
- The data theft incident affecting cloud data company Snowflake customers has been attributed to the UNC5537 threat actor.
- Incident response firm Mandiant says approximately 165 companies may have had their data stolen.
- The firm confirmed most of the impacted accounts had prior credential exposure that enabled attacker access.
Incident response firm Mandiant is working with multi-cloud data warehousing platform Snowflake to investigate the recent surge of data breaches affecting the cloud data company’s customers. The company notified around 165 customers about the account hacks that began in April, and the number of affected companies using Snowflake environments hasn’t been disclosed until now.
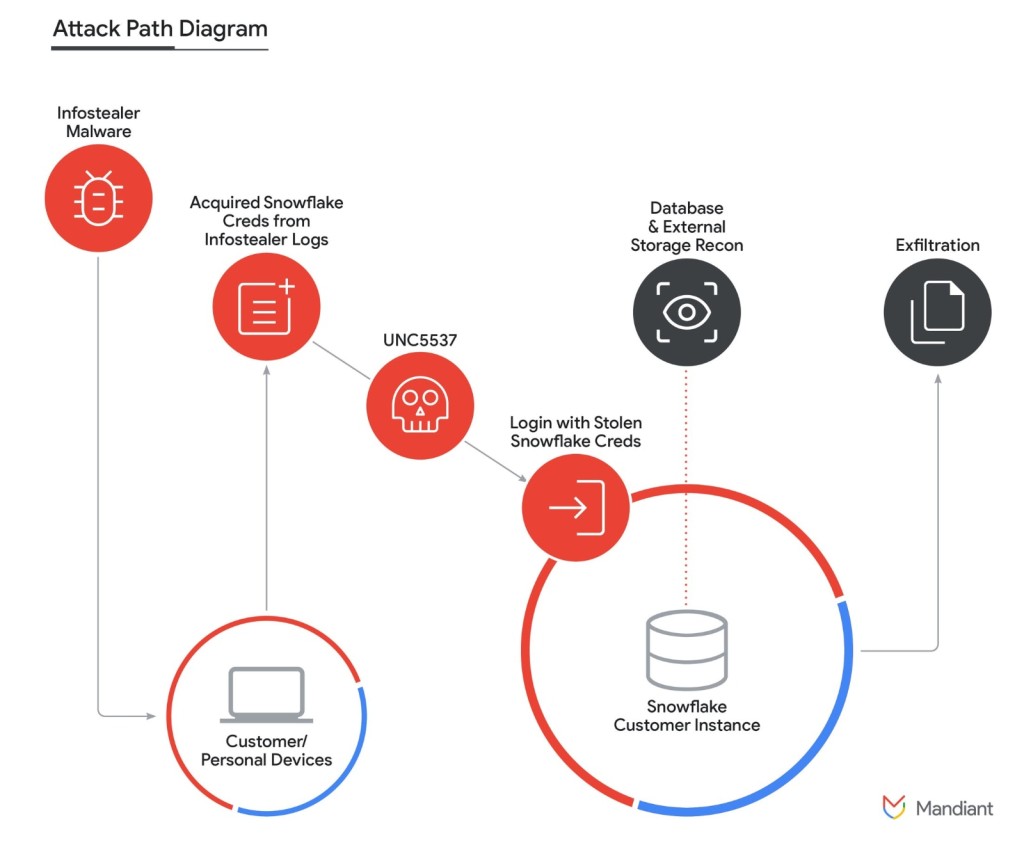
Mandiant has identified a threat campaign targeting Snowflake customer database instances containing large amounts of structured and unstructured data with the intent of data theft and extortion as “UNC5537.”
The malicious actor apparently compromised Snowflake enterprise instances to sell the stolen information on cybercrime forums and extort the victims via stolen client credentials, primarily obtained from various info-stealer malware campaigns that infected employee computers with access to their employer’s Snowflake environment.
Mandiant has now confirmed that the cybercriminals managed to gain access to Snowflake customer accounts that did not have multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled via leaked usernames and passwords of clients using Snowflake environments, exposed via several info-stealer malware variants, including VIDAR, RISEPRO, REDLINE, RACOON STEALER, LUMMA, and METASTEALER.
The company added that the impacted accounts did not have network allow lists in place to exclusively permit access from trusted locations and mentioned the root cause of the incident is related to exposed credentials, with at least 79.7% of the accounts having prior credential exposure.
Mandiant identified initial access to Snowflake customer instances often occurred via the native Web-based UI (SnowFlake UI AKA SnowSight) and/or command-line interface (CLI) tool (SnowSQL) running on Windows Server 2022, and a “rapeflake” attacker-named utility, tracked as FROSTBITE, most probably used for reconnaissance.
Mandiant observed the usage of both .NET and Java versions of FROSTBITE that interacted with the Snowflake .NET driver and the Snowflake JDBC driver, respectively, performing SQL recon activities, including listing users, current roles, current IPs, session IDs, and organization names. UNC5537 connects and runs queries via the publicly available database management utility DBeaver Ultimate.
Similar SQL commands were repeatedly executed across numerous customer Snowflake instances to stage and exfiltrate data – the SHOW TABLES command to perform reconnaissance, the SELECT command to download individual tables, the CREATE STAGE command, and the COPY INTO command, then compressing the results as a GZIP file before exfiltrating data via the GET command.
UNC5537 primarily used Mullvad or Private Internet Access (PIA) VPN IP addresses to access victim Snowflake instances, exfiltrating data via VPS systems from Moldovan provider ALEXHOST SRL (AS200019) and storing stolen victim data on several international VPS providers and the cloud storage provider MEGA.
November 2020 is the earliest info-stealer infection date observed associated with credentials leveraged by the threat actor, and hundreds of Snowflake customer credentials have been exposed via info-stealers since then. UNC5537 operates under various aliases on Telegram channels and cybercrime forums and has targeted hundreds of organizations worldwide, frequently for extortion.